Below are the real-time scenarios to use the Apex Batch job.
1) Say if you want to send an email 30 days before the contract expired to notify the owner that the contract is going to expire.
In this situation we will go
with Batch Apex, which will run as needed say daily and check all the contracts
which are expiring in next 30 days and send an email to the owner person.
Please note we can also create a Time-based workflow to achieve the above requirement however it doesn't run against existing records. The new rule only applies to records created or updated after the rule is activated.
2) Create a renewal opportunity base on contract end date.
3) Delete all the cases which have Status as “Closed” and Closed Reason as “No Action Needed” and Closed Date of Last Year.
Let’s see a practical example.
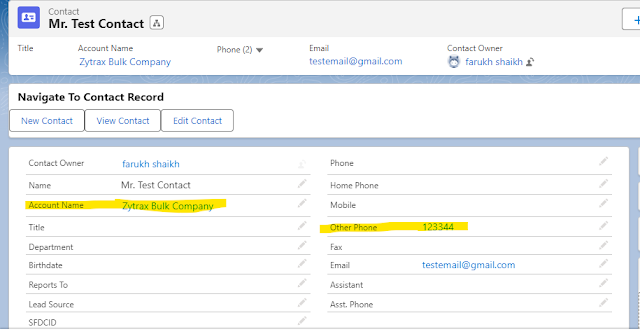
Let’s say you have a business requirement that states that all contacts for which
Account Billing Country is Australia must have their other phone number same as
that is present on the Account. Unfortunately, users are entering different
phone number in the other phone number.
Write a Batch Apex class that
ensures that this requirement is enforced.
public class UpdateContactCompanysPhone implements
Database.Batchable<sObject>, Database.Stateful {
public Database.QueryLocator
start(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
return
Database.getQueryLocator(
'SELECT ID, Phone,
(SELECT ID, OtherPhone FROM Contacts) FROM Account ' +
'Where BillingCountry
= \'Australia\''
);
}
public void
execute(Database.BatchableContext bc, List<Account> scope){
List<Contact>
contacts = new List<Contact>();
for (Account account :
scope) {
for (Contact contact :
account.contacts) {
contact.OtherPhone =
account.Phone;
contacts.add(contact);
}
}
update contacts;
}
public void
finish(Database.BatchableContext bc){
System.debug('Finish
Executed');
}
}
@isTest
private class UpdateContactCompanysPhoneTestClass {
@testSetup
static void setup() {
List<Account>
accounts = new List<Account>();
List<Contact>
contacts = new List<Contact>();
for (Integer
i=0;i<1;i++) {
accounts.add(new
Account(name='Account '+i,
billingcity='Sydney', billingcountry='Australia'));
}
insert accounts;
for (Account account :
[select id from account]) {
contacts.add(new
Contact(firstname='Test',
lastname='Contact', accountId=account.id));
}
insert contacts;
}
@isTest static void test() {
Test.startTest();
UpdateContactCompanysPhone
updcon = new UpdateContactCompanysPhone();
Id batchId =
Database.executeBatch(updcon);
Test.stopTest();
System.assertEquals(1,
[select count() from contact]);
}
}
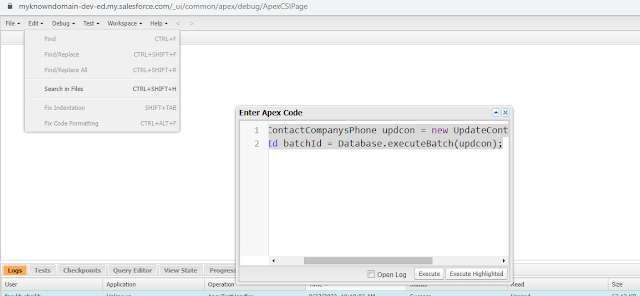
To run the above batch class,
Paste the below code in
developer console “Execute Anonymous Window”.
UpdateContactCompanysPhone updcon = new
UpdateContactCompanysPhone();
Id batchId = Database.executeBatch(updcon);
You can also schedule the above
class using a scheduler class to run daily.
Scheduling apex job:
To Schedule the batch class,
you need a class which implements schedulable interface,
global class schedulebatch implements schedulable{
global void
execute(Schedulablecontext sc)
{
UpdateContactCompanysPhone
acc=new UpdateContactCompanysPhone ();
//Database.executeBatch(instance,size);
Database.executeBatch(acc,200);
}
}
Now, you can schedule class schedulebatch
from User Interface,
Setup>develop>apex classes> schedule apex.
Best Practices:
Only use Batch Apex if you have
more than one batch of records. If you don't have enough records to run more
than one batch, you are probably better off using Queueable Apex.
Tune any SOQL query to gather
the records to execute as quickly as possible.
Minimize the number of
asynchronous requests created to minimize the chance of delays.
Use extreme care if you are
planning to invoke a batch job from a trigger. You must be able to guarantee
that the trigger won’t add more batch jobs than the limit.

No comments:
Post a Comment